Hardware Crypto Wallet: A Complete Guide
In today’s digital age, securing cryptocurrency holdings is crucial. To combat evolving cyber threats, tech-savvy individuals rely on hardware wallets for robust protection. These powerful standalone devices, resembling USB sticks, safeguard private keys – the essential passwords granting access to cryptocurrencies. Our comprehensive guide explains how hardware wallets work, their security features, and steps to choose the right one. Discover the benefits, risks, and best practices to confidently safeguard and manage your digital wealth, whether you’re an experienced crypto enthusiast or new to digital currencies.
What is a Hardware Wallet
A hardware wallet is a specialized device designed to securely store and manage your private keys, which are essential for accessing and managing your cryptocurrencies. It is considered one of the most secure ways to protect your digital assets. Unlike software or web-based wallets, which are permanently connected to the internet and can be vulnerable to hacking attempts, hardware wallets keep your private keys offline in an isolated environment. They are physical devices, often resembling a USB stick, that act as stripped-down, single-purpose computers.
By storing your private keys in a hardware wallet, you ensure that they are not directly exposed to the internet, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access or theft. When you need to perform a transaction, you briefly connect the hardware wallet to a computer or mobile device to sign the transaction digitally using your private key. This digital signature is then securely uploaded to the blockchain through a cryptographic bridge. Additionally, hardware wallets offer compatibility with multiple blockchain networks, allowing users to interact with different cryptocurrencies. They typically support popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, among others.
While hardware wallets offer strong security, they may be less convenient compared to mobile or software wallets in certain situations. They require physical access to the device for transactions and usually involve a higher upfront cost, starting around $40 and going up to $200. However, for tech-savvy individuals who prioritize the security of their digital assets and want to have full control over their private keys, hardware wallets are an excellent choice.
How does a Hardware Wallet work
A hardware wallet functions as a simplified computer created exclusively for cryptocurrency transactions. It incorporates a compact screen and a limited number of buttons. A notable advantage is its deliberate lack of direct internet connectivity, which significantly bolsters its security against potential hacker intrusions.

When engaging in cryptocurrency transactions such as spending, trading, or sending/receiving digital assets through a wallet, the transaction requires the “signing” process using a private key. Within a hardware wallet, this signing procedure occurs internally, facilitated by a crypto bridge – a straightforward software that enables seamless interaction between the hardware wallet and the blockchain.
Here’s how a hardware wallet works:
- Private Key Generation: When you set up a hardware wallet, it generates a pair of cryptographic keys – a public key and a private key. The private key is kept within the secure element of the hardware wallet and never leaves the device.
- Secure Element: The hardware wallet contains a specialized chip known as the secure element. This chip is designed to securely store and protect the private keys from physical tampering and unauthorized access.
- PIN Code: To access the private keys stored in the hardware wallet, you must enter a PIN code. This PIN acts as an additional layer of security and prevents unauthorized access to your cryptocurrencies even if the device is lost or stolen.
- Transaction Signing: When you want to send cryptocurrency from your hardware wallet, the device generates the transaction details and then signs it with your private key within the secure element. This process ensures that the transaction is authentic and approved by the owner of the wallet.
- Recovery Seed: During the initial setup, the hardware wallet provides you with a recovery seed – a sequence of 12 to 24 words. This recovery seed acts as a backup of your private keys and allows you to restore access to your cryptocurrencies in case the hardware wallet is lost, damaged, or needs to be reset.
- Offline Operation: Hardware wallets operate offline, which means they are not directly connected to the internet during normal use. This offline operation significantly reduces the risk of remote attacks and hacking attempts on your private keys.
- Compatibility and Apps: Hardware wallets support various cryptocurrencies, and you can manage specific coins by installing dedicated apps on the device. These apps ensure that only the relevant private keys associated with a particular cryptocurrency are exposed when needed.
- Verification: To ensure the authenticity of the hardware wallet, manufacturers often provide verification features, such as a check mark or other indicators, to confirm that the device is genuine and has not been tampered with.
Here is a step-by-step explanation of how to use a hardware wallet:
- Unboxing: Open the package and ensure you received an authentic and genuine hardware wallet from the manufacturer.
- Charging (if applicable): Some hardware wallets are rechargeable and may require charging before use.
- Connect to Device: Connect the hardware wallet to your computer or mobile device using the provided cable.
- Initialize the Wallet: Follow the on-screen instructions to initialize the hardware wallet. This may include setting a PIN code and writing down the 24-word recovery seed.
- Install Apps: Install the necessary apps for the cryptocurrencies you want to manage on the hardware wallet.
- Backup Recovery Seed: Carefully write down the 24-word recovery seed on the provided cards or a secure piece of paper. Store it in multiple safe and separate locations.
- Confirm Setup: Once the setup is complete, verify that you can access your wallet and funds.
When setting up a hardware wallet, the initial steps involve creating a one-of-a-kind PIN code and generating a recovery phrase. This recovery phrase serves as a backup for your wallet and comprises a sequence of words. Its purpose is to aid in the restoration of your wallet and the recovery of your funds in the event of loss or theft. By securely generating and storing private keys in an offline environment, hardware wallets ensure protection against possible online risks. Private keys, which function as crucial passwords granting access to your cryptocurrency, must always be safeguarded and kept confidential.
To initiate a transaction using a hardware wallet, start by connecting the device to your computer or smartphone. Unlock the hardware wallet using your PIN code and proceed to input the recipient’s public key and the desired amount for the transaction. The hardware wallet validates the transaction details and utilizes your private key to sign the transaction. This process generates a unique digital signature that ensures the transaction’s authenticity and enables its recording on the blockchain.
How to Choose a Hardware Wallet
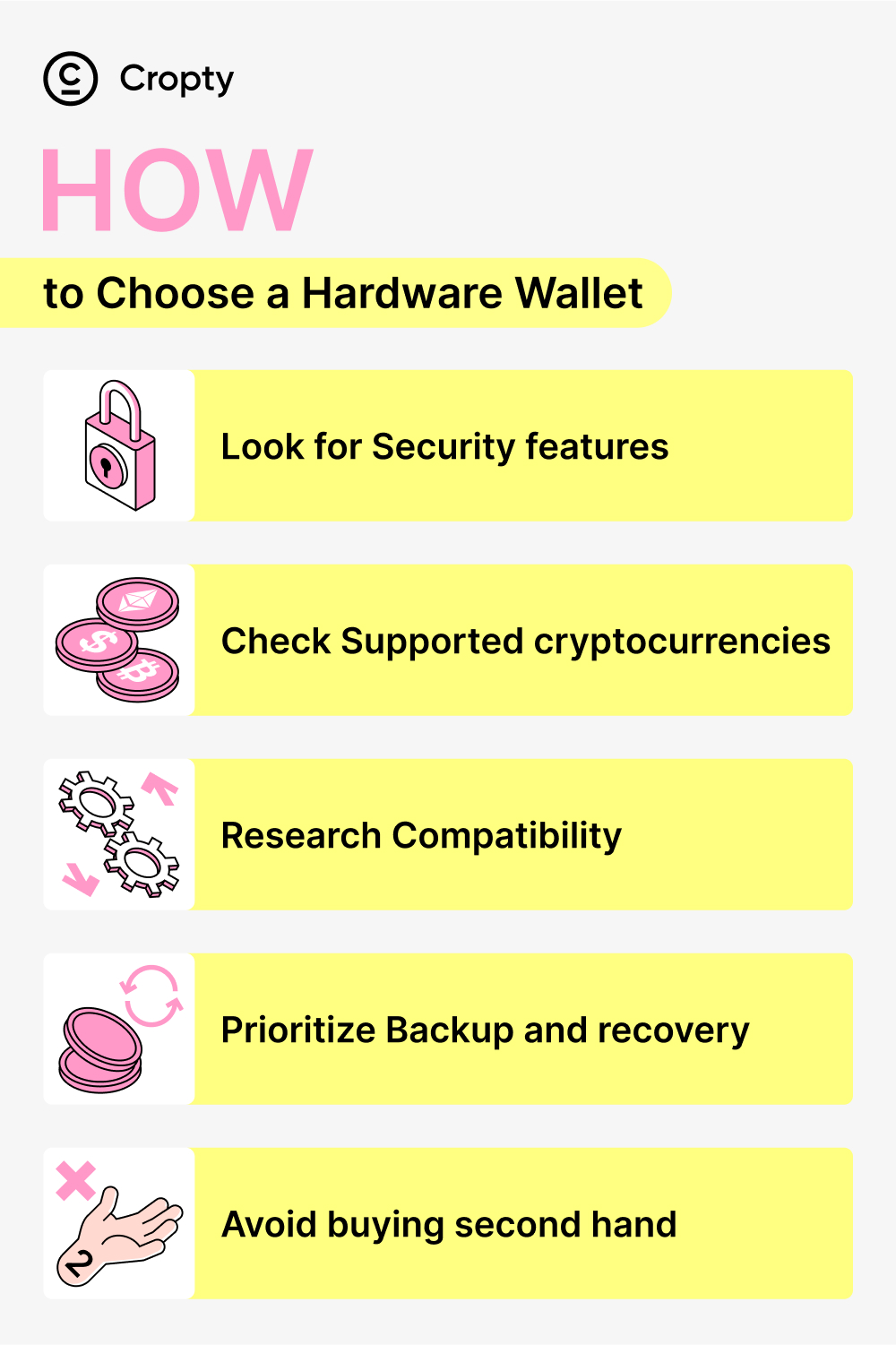
Selecting the appropriate hardware wallet is crucial to ensure optimal user experience and security at a reasonable price. By carefully assessing your requirements, you can choose a hardware wallet that best fits your needs. Here are steps to help you make the right decision:
- Prioritize security features: Give preference to hardware wallets that offer strong security features such as PIN codes, passphrase protection, and biometric authentication. It is important that the device employs advanced encryption to safeguard your private keys and defend against hacking attempts and cyber threats.
- Verify supported cryptocurrencies: Ensure that the hardware wallet supports the specific cryptocurrencies you plan to invest in. Not all wallets are compatible with every cryptocurrency, so it is essential to review the manufacturer’s compatibility list before purchasing.
- Assess compatibility: Consider whether the hardware wallet is compatible with other wallet interfaces or applications that you frequently use. For instance, if you engage in decentralized finance (DeFi) or utilize NFT apps that require integration with wallet interfaces like MetaMask, choose a hardware wallet that seamlessly integrates with those interfaces.
- Emphasize backup and recovery options: Confirm that the hardware wallet provides reliable backup and recovery mechanisms. It is crucial to have a backup plan in case the device is lost or damaged. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to securely back up your private keys and seed phrase. Having proper backup options is vital to protect your funds.
- Avoid purchasing second-hand: It is highly recommended to buy a new hardware wallet instead of opting for a second-hand one. Second-hand wallets might have been tampered with, posing a risk to your assets. Although saving money might be tempting, the value of the assets stored in the wallet usually outweighs any potential savings from buying second-hand.
By considering these factors, you can choose a hardware wallet that offers robust security features, supports your desired cryptocurrencies, integrates well with relevant applications, and provides reliable backup and recovery options. This will ensure peace of mind as you securely manage your digital assets.
Best Hardware Wallets
| Wallet | Supported Coins | Screen | Price |
| Ledger Nano S Plus | 5,500+ | 128×64 px screen | $79 |
| Trezor Model T | 1,000+ | touchscreen | $219 |
| KeepKey | 7,000+ | 256×64 px screen | $49 |
| Tangem | 6,000+ | no | $44 |
Related: 10 Best Cold Wallets for Crypto Storage of December 2023
Hardware Wallets Pros and Cons
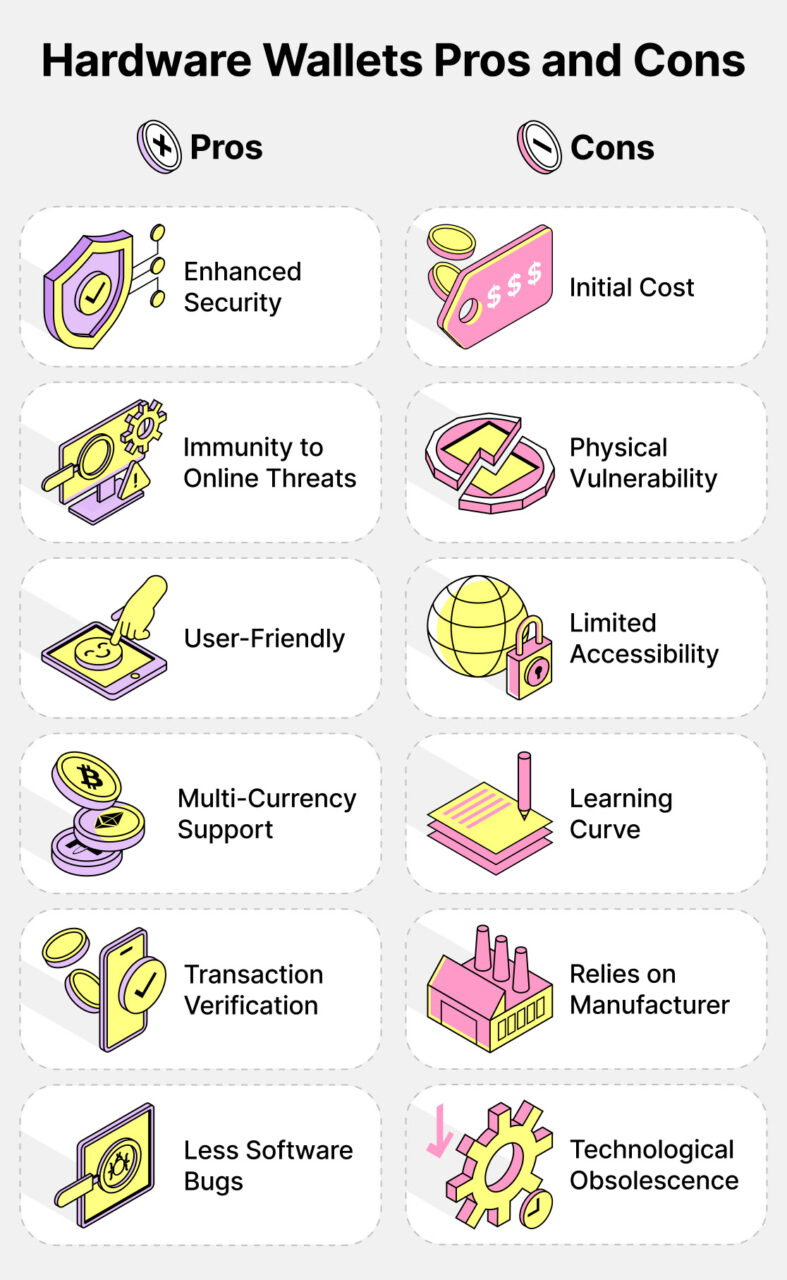
Pros:
- Enhanced Security:
- Pro: Hardware wallets provide a higher level of security by keeping private keys offline, minimizing the risk of online hacking attempts.
- Immunity to Online Threats:
- Pro: Being offline most of the time, hardware wallets are less susceptible to online threats such as phishing attacks and malware.
- User-Friendly:
- Pro: Hardware wallets are designed with user-friendliness in mind, often featuring intuitive interfaces that make it easier for both beginners and experienced users to navigate.
- Multi-Currency Support:
- Pro: Many hardware wallets support a wide range of cryptocurrencies, allowing users to store and manage various assets in a single device.
- Transaction Verification:
- Pro: Hardware wallets typically include a secure confirmation process for transactions, ensuring users have full control and visibility over their crypto transactions.
- Limited Software Bugs:
- Pro: Due to their simplicity and focused functionality, hardware wallets are less prone to software bugs or vulnerabilities compared to software wallets.
- Technological Obsolescence:
- Pro: Hardware wallets can remain functional for an extended period without becoming technologically obsolete, providing long-term value.
Cons:
- Initial Cost:
- Con: Hardware wallets often have an upfront cost, which may be a barrier for some users, especially those who are just getting started with cryptocurrency.
- Physical Vulnerability:
- Con: Despite enhanced security, hardware wallets can be susceptible to physical damage, loss, or theft. Users need to take precautions to safeguard the physical device.
- Limited Accessibility:
- Con: Unlike software wallets that can be accessed from various devices, hardware wallets are tied to the physical device, making it less accessible when needed.
- Learning Curve:
- Con: Some users, especially beginners, may find it challenging to set up and use a hardware wallet due to its security features, leading to a learning curve.
- Relies on Manufacturer:
- Con: Users depend on the manufacturer’s integrity and security practices. If the manufacturer experiences a breach or compromise, it could impact the security of the hardware wallet.
- Less Software Bugs:
- Con: While fewer software bugs are a pro, this can also be a con as it may lead to slower adaptation to emerging technologies or updates in the cryptocurrency space.
Hardware Wallet Security
Private keys play a vital role in the security of hardware wallets. They are unique strings of characters that serve as digital signatures or passwords to access and manage cryptocurrency holdings. When creating a digital wallet, private and public keys are generated. The public key, or wallet address, allows others to send crypto to your wallet, while the private keys grant direct access to the wallet and should never be shared.
Hardware wallets are generally considered to be one of the most secure ways to store and manage cryptocurrencies. They offer several advantages over other forms of cryptocurrency storage:
- Complete Control over Private Keys: Hardware wallets provide you with full ownership and control over your private keys, which are essential for accessing and managing your cryptocurrency holdings. Unlike keeping your assets on an exchange, where the exchange holds the private keys, a hardware wallet ensures that only you have access to your funds.
- Enhanced Security Measures: Hardware wallets employ multiple security features, such as secure chip elements, air gap technology, anti-tamper mechanisms, and even biometrics, to protect your private keys and ensure the safety of your cryptocurrencies.
- Immunity to Online Threats and Malware: Since hardware wallets operate offline and keep your private keys stored securely in cold storage, they are immune to online threats and malware that can target software wallets or exchanges.
- Improved Privacy: Hardware wallets typically do not require any personal information during setup, providing enhanced privacy compared to crypto exchanges or some software wallets that may ask for identification.
However, there are some cons to consider:
- Cost: Hardware wallets come with a price, ranging from around $40 to several hundred dollars, depending on the features and brand. While the cost is justified for the security it provides, it may still be a factor for some users.
- Learning Curve: Hardware wallets may have a steeper learning curve compared to software wallets or exchanges, which could be challenging for less tech-savvy individuals. However, many hardware wallets are designed with user-friendly interfaces to mitigate this issue.
- Potential Loss or Theft: Just like physical objects, hardware wallets can be lost, damaged, or stolen. However, as long as you have your recovery seed or private key, you can recover your funds on a new device.
- Vulnerability to Scams: While hardware wallets offer strong security for your cryptocurrencies, they do not protect you from other types of scams or phishing attempts. Users should remain vigilant and practice good security habits, even with a hardware wallet.

Here are solutions to mitigate common security threats related to hardware wallets:
- Physical Security Threats: Protect hardware wallets from physical risks such as loss, theft, or damage. Use a secure seed phrase, as it allows the recovery of crypto assets in case of loss or damage. Be cautious of tampering or poor device configuration that could compromise security.
- Power Glitching: Prevent fault-injection attacks by manipulating voltage modulations to disrupt the wallet’s behavior. To counter this, maintain physical control over the hardware wallet and be vigilant against any suspicious activities.
- Firmware Risks: Purchase hardware wallets from reputable manufacturers and validate firmware updates before installation. This minimizes the risk of attackers modifying the firmware to extract private keys or compromise the device’s security.
- Side-Channel Attacks: Safeguard against side-channel attacks by ensuring the hardware wallet is from a trusted source and has implemented countermeasures against such vulnerabilities. Maintain control over physical access to the device to mitigate the risk of this type of attack.
- Social Engineering Dangers: Stay vigilant against social engineering attacks, such as phishing emails or scams aimed at tricking users into revealing private keys. Educate yourself on common social engineering tactics and be cautious when sharing sensitive information.
To those considering buying a hardware wallet, it is essential to understand that hardware wallets significantly enhance the security of your cryptocurrencies. They are worth the investment if you want to have complete control over your funds and minimize the risk of online attacks. However, it’s crucial to stay informed about potential scams and best security practices to ensure your digital assets remain safe and protected. Always research and choose reputable hardware wallet brands, follow proper setup procedures, and keep your recovery seed or private key secure and confidential.